Today’s modern workplaces are evolving fast thanks to the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors. These small devices are helping companies keep track of their spaces, resources, and how their employees are doing. They provide important data that enables a shift from merely reacting to situations to making informed, intelligent decisions based on that data.
It’s not just about working more efficiently, either. This tech is also making a real difference in how employees feel at work by improving the indoor environment. With precise control over lighting and air quality, these sensors help create a healthier space, reducing health risks and improving focus. Plus, they’re crucial for sustainability efforts. By monitoring energy use, water consumption, and waste, they help organizations pinpoint where they can save resources and make a real impact.
This data-driven strategy cuts down on costs and supports environmental goals, making it easier for companies to track their ecological footprint. In the end, with IoT integration, companies can create better working conditions, save resources, and enhance productivity, giving employees an environment where they can really excel without unnecessary distractions.
Here are 13 different types of sensors that can bring well-being, sustainability, and strategic insights into the modern workplace.
The Strategic Advantages of Sensor Implementation
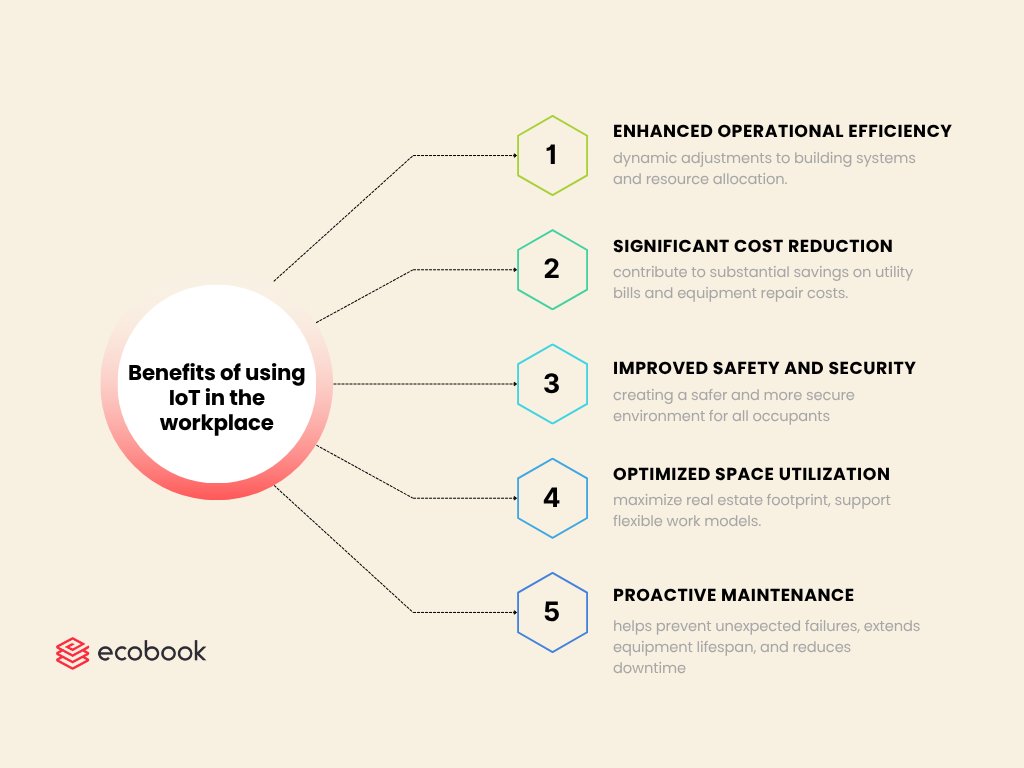
Implementing IoT sensors within the workplace offers a multitude of benefits that directly impact operational efficiency, financial performance, and human capital:
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Real-time data from sensors allows for dynamic adjustments to building systems and resource allocation, streamlining daily operations and reducing manual intervention while increasing employee comfort and well-being.
- Significant Cost Reduction: By optimizing energy consumption and facilitating predictive maintenance, IoT sensors contribute to substantial savings on utility bills and equipment repair costs, directly impacting the operating expenses and the bottom line.
- Improved Safety and Security: Sensors provide continuous monitoring for potential hazards, unauthorized access, and environmental risks, creating a safer and more secure environment for all occupants.
- Optimized Space Utilization: Accurate insights into space occupancy and usage patterns enable organizations to maximize their real estate footprint, supporting flexible work models and efficient office design.
- Proactive Maintenance and Asset Management: Monitoring the performance and condition of critical assets helps prevent unexpected failures, extends equipment lifespan, and reduces downtime.
Key Categories of IoT Sensors in the Workplace
The diverse range of IoT sensors available addresses various operational needs:
- Environmental Sensors: These sensors are crucial for maintaining optimal indoor conditions. They directly impact employee comfort, health, and compliance with environmental standards, contributing to a better working environment and therefore higher productivity.
- Temperature and Humidity Sensors: Regulate HVAC systems to ensure occupant comfort and energy efficiency.
- Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Sensors: Monitor CO2, VOCs, and particulate matter to ensure a healthy and productive environment.
- Light Sensors: Adjust lighting systems automatically to optimize illumination and conserve energy.
- Noise Sensors: Provide data on acoustic levels to support a conducive work atmosphere.
- Occupancy and Space Utilization Sensors: Essential for efficient space management and agile work strategies. These sensors optimize office real estate expenditure, support flexible working arrangements, and inform strategic space planning.
- Occupancy Sensors (PIR, ToF, Radar-based, Ultrasonic, Camera-based): Detect presence to automate lighting/HVAC, manage desk/room bookings, and inform cleaning schedules. These can be linked to meeting room booking system and desk booking systems to detect occupancy rates.
- People Counting Sensors: Track foot traffic to understand flow and manage density within facilities.
- Security and Safety Sensors: Fundamental for protecting personnel and assets. These sensors ensure compliance with safety regulations, minimize risks, and protect organizational assets and personnel.
- Motion Sensors, Door/Window Contact Sensors: Enhance physical security and alert to unauthorized access.
- Smoke/Fire and Carbon Monoxide (CO) Detectors: Provide critical early warnings for life-threatening hazards.
- Leak Detection Sensors (Water/Gas): Prevent property damage and ensure a safe environment by detecting spills or gas leaks.
- Asset Tracking and Management Sensors: Facilitate efficient monitoring and maintenance of equipment. These sensors reduce operational downtime, extend asset lifespan, and optimize maintenance schedules.
- Proximity Sensors, Vibration Sensors: Monitor equipment operational status and predict maintenance needs.
- Temperature and Current Monitoring Sensors: Track equipment performance to prevent overheating and identify energy inefficiencies.
- Wearable Sensors (Context-Specific): Employed in roles requiring enhanced worker safety monitoring. These sensors are crucial for mitigating risks in high-hazard environments and ensuring prompt response to incidents.
- Biometric Sensors (e.g., heart rate), Fall Detection Sensors: Monitor worker health and safety in hazardous environments.
- Location Tracking Sensors (GPS/BLE/RFID): Enhance emergency response and optimize workflows in large facilities.
Driving Senior Management Decision-Making with Sensor Data
The true power of IoT sensor implementation lies in its ability to provide actionable intelligence for senior management. This data moves decision-making from intuition to empirical evidence, impacting core strategic areas:
- Real Estate Portfolio Optimization: Granular data on space utilization allows management to right-size their real estate footprint. This can lead to substantial savings on leases or property taxes, inform decisions on expansion versus consolidation, and guide the design of future workspaces that truly align with employee needs and work styles.
- Operational Cost Reduction: Detailed insights into energy consumption, equipment performance, and resource usage identify inefficiencies previously unseen. Management can then implement targeted automation, modify operational schedules, and negotiate better utility rates based on accurate consumption patterns, leading to verifiable cost savings.
- Employee Experience and Retention: By providing objective data on environmental conditions (air quality, temperature, noise), management can proactively address factors impacting employee comfort and health. A more pleasant and healthier work environment directly contributes to higher employee satisfaction, reduced absenteeism, and improved talent retention.
- Strategic Capital Investment: Sensor data provides a clear picture of asset performance and lifespan. This enables more informed capital expenditure decisions, ensuring investments in new equipment or infrastructure are based on genuine need and potential return on investment, rather than scheduled replacements or reactive purchases.
- Sustainability and ESG Reporting: For organizations committed to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals, sensor data offers measurable metrics for resource consumption (energy, water). This data is invaluable for reporting progress on sustainability initiatives, enhancing corporate reputation, and demonstrating commitment to responsible business practices.
Conclusion
In essence, IoT sensors are not merely technological enhancements; they are strategic tools that provide senior management with the empirical evidence needed to make informed, impactful decisions across real estate, finance, human resources, and operational domains. Their implementation marks a significant step towards creating intelligent, adaptive, and highly efficient workplaces.
Further Reading
Using Occupancy Sensors To Control Meeting Rooms